What Are The Principal Reasons For Over-Pronation
Overview
Overpronation is the exaggerated inward rolling of the foot and ankle, which can lead to a collapsed arch and flat feet. Many people overpronate and do not even realize it; one way to tell is to simply look at the foot and see how it is placed on the ground when standing in a neutral position. Another way is to wet the bottom of the foot and step on a piece of paper. If the entire imprint of the foot is shown, it means you overpronate.
Causes
Congenital "Flat Feet" - an individual may be born with feet that lack an appropriately supportive arch thereby predisposing the individual to this foot condition. Excessive Weight (Obesity) Too much weight on the foot from either obesity or pregnancy may be a factor. Repetitive Impact walking on flat, hard surfaces continuously places unnatural stress on the foot arch.
Symptoms
Common conditions seen with overpronation include heel pain or plantar fasciitis, achilles tendonopathy, hallus valgus and or bunions, patellofemoral pain syndrome, Iliotibial band pain syndrome, low back pain, shin splints, stress fractures in the foot or lower leg.
Diagnosis
Do the wet foot test. Get your feet wet and walk along a paved surface or sand and look at the footprints you leave. If you have neutral feet you will see a print of the heel with a thin strip connecting to your forefoot, but if you're overpronating your foot print will look a bit like a giant blob with toes.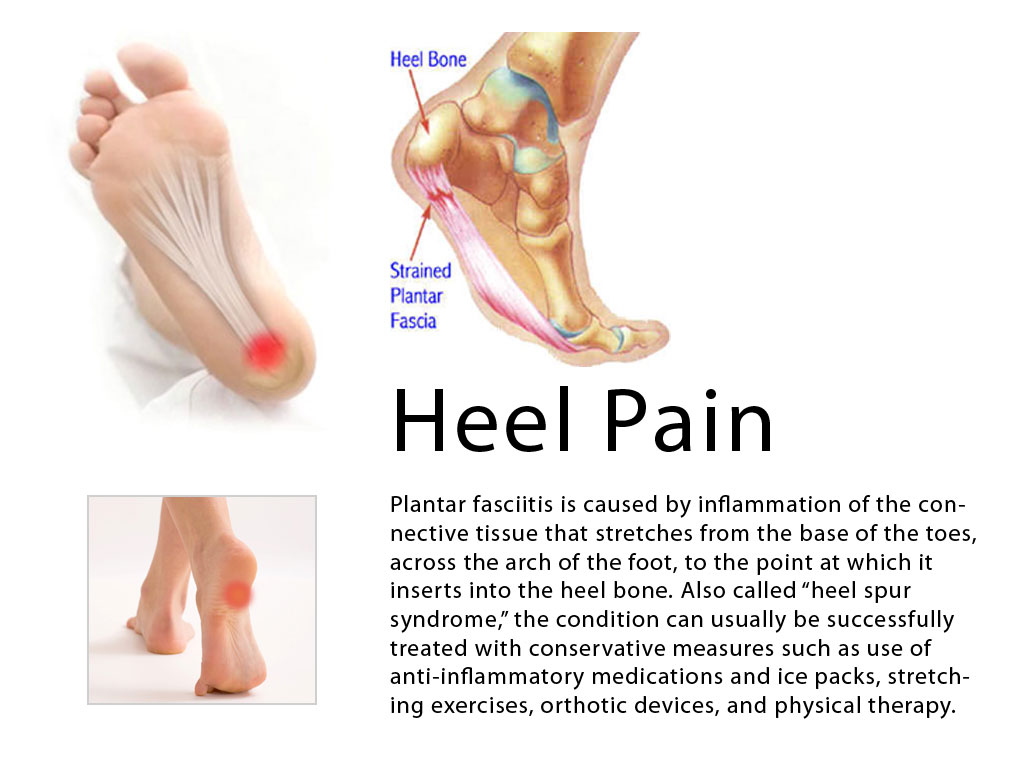
Non Surgical Treatment
Solutions typically presented will include physical therapy sessions, prolonged prescription drug regimens, occasionally non-traditional approaches like holistic medicine and acupuncture. These options can provide symptom relief in the short term for some patients. However, these treatment methods cannot correct the internal osseous misalignment. Ligaments are not effective in limiting the motion of the ankle bone when excessive joint motion is present. Furthermore, there is not a single, specific ligament that is "too tight" that needs to be "stretched out." The muscles supporting the bones are already being "over-worked" and they cannot be strengthened enough to realign these bones. There is no evidence to suggest that any of these measures are effective in re-establishing or maintaining the normal joint alignment and function.
Surgical Treatment
Subtalar Arthroereisis. Primary benefit is that yje surgery is minimally invasive and fully reversible. the primary risk is a high chance of device displacement, generally not tolerated in adults.
An implant is pushed into the foot to block the excessive motion of the ankle bone. Generally only used in pediatric patients and in combination with other procedures, such as tendon lengthening. Reported removal rates vary from 38% - 100%, depending on manufacturer.
Overpronation is the exaggerated inward rolling of the foot and ankle, which can lead to a collapsed arch and flat feet. Many people overpronate and do not even realize it; one way to tell is to simply look at the foot and see how it is placed on the ground when standing in a neutral position. Another way is to wet the bottom of the foot and step on a piece of paper. If the entire imprint of the foot is shown, it means you overpronate.

Causes
Congenital "Flat Feet" - an individual may be born with feet that lack an appropriately supportive arch thereby predisposing the individual to this foot condition. Excessive Weight (Obesity) Too much weight on the foot from either obesity or pregnancy may be a factor. Repetitive Impact walking on flat, hard surfaces continuously places unnatural stress on the foot arch.
Symptoms
Common conditions seen with overpronation include heel pain or plantar fasciitis, achilles tendonopathy, hallus valgus and or bunions, patellofemoral pain syndrome, Iliotibial band pain syndrome, low back pain, shin splints, stress fractures in the foot or lower leg.
Diagnosis
Do the wet foot test. Get your feet wet and walk along a paved surface or sand and look at the footprints you leave. If you have neutral feet you will see a print of the heel with a thin strip connecting to your forefoot, but if you're overpronating your foot print will look a bit like a giant blob with toes.

Non Surgical Treatment
Solutions typically presented will include physical therapy sessions, prolonged prescription drug regimens, occasionally non-traditional approaches like holistic medicine and acupuncture. These options can provide symptom relief in the short term for some patients. However, these treatment methods cannot correct the internal osseous misalignment. Ligaments are not effective in limiting the motion of the ankle bone when excessive joint motion is present. Furthermore, there is not a single, specific ligament that is "too tight" that needs to be "stretched out." The muscles supporting the bones are already being "over-worked" and they cannot be strengthened enough to realign these bones. There is no evidence to suggest that any of these measures are effective in re-establishing or maintaining the normal joint alignment and function.
Surgical Treatment
Subtalar Arthroereisis. Primary benefit is that yje surgery is minimally invasive and fully reversible. the primary risk is a high chance of device displacement, generally not tolerated in adults.
An implant is pushed into the foot to block the excessive motion of the ankle bone. Generally only used in pediatric patients and in combination with other procedures, such as tendon lengthening. Reported removal rates vary from 38% - 100%, depending on manufacturer.