What Are The Signals Of Calcaneal Spur
:origin()/pre14/f8b9/th/pre/f/2012/020/e/8/skadi_fairy_queen_fanart_by_calcaneus-d4n0dmb.jpg)
Overview
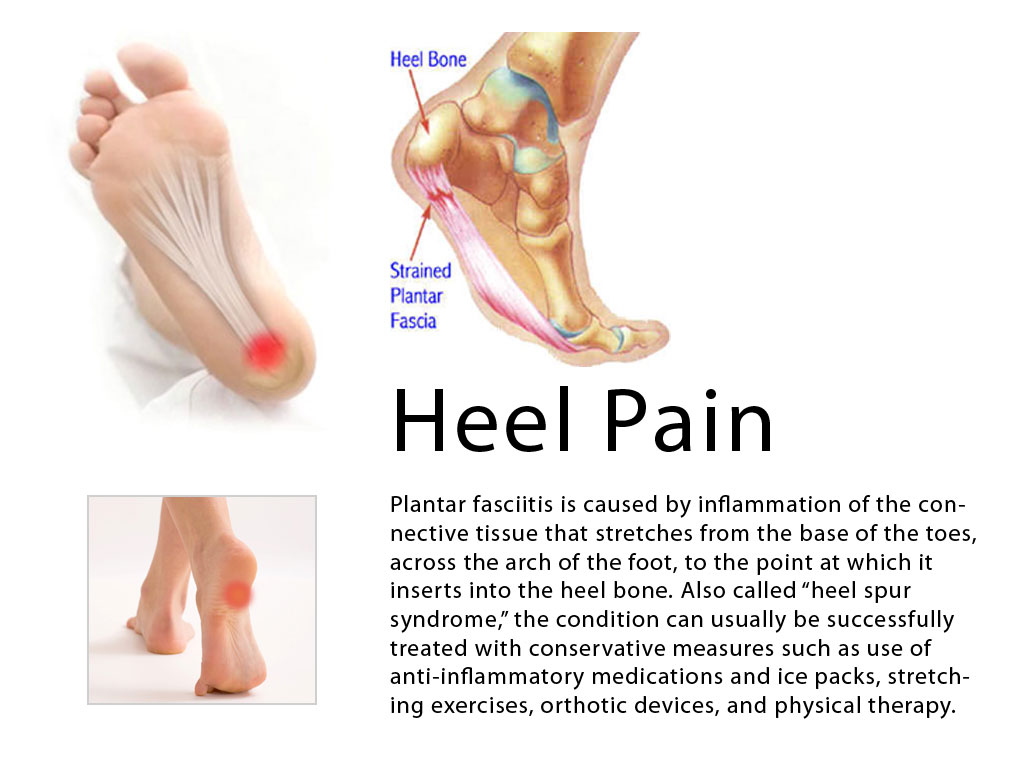
A bone spur (osteophyte) is a bony growth that forms along the edge of normal bone in response to wear and tear, most frequently in the joints. A heel spur is a bone spur of the heel bone, which causes heel pain by rubbing on the achilles tendon or other soft tissues.
Causes
The cause of heel spurs is excessive strain placed on the plantar fascia over a long period of time, as a result of different factors. These factors include incorrect gait, being overweight, ageing or being in a job that requires a lot of standing on hard floors. It is usually a combination of any of these factors that will bring on the development of heel spurs.

Symptoms
Major symptoms consist of pain in the region surrounding the spur, which typically increases in intensity after prolonged periods of rest. Patients may report heel pain to be more severe when waking up in the morning. Patients may not be able to bear weight on the afflicted heel comfortably. Running, walking, or lifting heavy weight may exacerbate the issue.
Diagnosis
Because the diagnosis of heel spurs can be confused with tarsal tunnel syndrome (as described earlier), most surgeons advocate performing a tarsal tunnel release (or at least a partial tarsal tunnel release) along with the plantar fascia release. This surgery is about 80percent successful in relieving pain in the small group of patients who do not improve with conservative treatments.
Non Surgical Treatment
If pain and other symptoms of inflammation-redness, swelling, heat-persist, you should limit normal daily activities and contact a doctor of podiatric medicine. The podiatric physician will examine the area and may perform diagnostic X-rays to rule out problems of the bone. Early treatment might involve oral or injectable anti-inflammatory medication, exercise and shoe recommendations, taping or strapping, or use of shoe inserts or orthotic devices. Taping or strapping supports the foot, placing stressed muscles and tendons in a physiologically restful state. Physical therapy may be used in conjunction with such treatments. A functional orthotic device may be prescribed for correcting biomechanical imbalance, controlling excessive pronation, and supporting of the ligaments and tendons attaching to the heel bone. It will effectively treat the majority of heel and arch pain without the need for surgery. Only a relatively few cases of heel pain require more advanced treatments or surgery. If surgery is necessary, it may involve the release of the plantar fascia, removal of a spur, removal of a bursa, or removal of a neuroma or other soft-tissue growth.
Surgical Treatment
Have surgery if no other treatments work. Before performing surgery, doctors usually give home treatments and improved footwear about a year to work. When nothing else eases the pain, here's what you need to know about surgical options. Instep plantar fasciotomy. Doctors remove part of the plantar fascia to ease pressure on the nerves in your foot. Endoscopy. This surgery performs the same function as an instep plantar fasciotomy but uses smaller incisions so that you'll heal faster. However, endoscopy has a higher rate of nerve damage, so consider this before you opt for this option. Be prepared to wear a below-the-knee walking cast to ease the pain of surgery and to speed the healing process. These casts, or "boots," usually work better than crutches to speed up your recovery time.
Best Remedy For Bursitis Of The Foot
Bursae (two or more bursa) are small, fluid-filled sacs that cushion the bones, tendons and muscles surrounding your joints. They contain a lubricating fluid that reduces friction, allowing tissues in the body to glide past each other smoothly. Imagine the bursa as a protective layer that helps keep a tendon or muscle from fraying or getting aggravated as it eases over a bone or around a corner. Bursitis is a condition that occurs when a bursa becomes inflamed: irritated, red and filled with more fluid than normal.
Causes
The most common causative organism is Staphylococcus aureus (80% of cases), followed by streptococci. However, many other organisms have been implicated in septic bursitis, including mycobacteria (both tuberculous and nontuberculous strains), fungi (Candida), and algae (Prototheca wickerhamii). Factors predisposing to infection include diabetes mellitus, steroid therapy, uremia, alcoholism, skin disease, and trauma. A history of noninfectious inflammation of the bursa also increases the risk of septic bursitis.
Symptoms
Achiness or stiffness in the affected joint. Worse pain when you press on or move the joint. A joint that looks red and swollen (especially when the bursae in the knee or elbow are affected). A joint that feels warm to the touch, compared to the unaffected joint, which could be a sign that you have an infection in the bursa. A ?squishy? feeling when you touch the affected part. Symptoms that rapidly reappear after an injury or sharp blow to the affected area.
Diagnosis
Medical examination is not necessarily required in light cases where the tenderness is minimal. In all cases where smooth improvement is not experienced, medical attention should be sought as soon as possible to exclude a (partial) rupture of the Achilles tendon or rupture of the soleus muscle. This situation is best determined by use of ultrasound scanning, as a number of injuries requiring treatment can easily be overlooked during a clinical examination (Ultrasonic image). Ultrasound scanning enables an evaluation of the extent of the change in the tendon, inflammation of the tendon (tendinitis), development of cicatricial tissue (tendinosis), calcification, inflammation of the tissue surrounding the tendon (peritendinitis), inflammation of the bursa (bursitis), as well as (partial) rupture.
Non Surgical Treatment
The most important factor in healing bursitis is resting your foot and ankle. This can be difficult when you have to carry on with daily activities, but resting and elevating your foot whenever you can is recommended. During your recovery you will probably have to modify or avoid the activities that stress your bursa until your pain and inflammation settle.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery to remove the damaged bursa may be performed in extreme cases. If the bursitis is caused by an infection, then additional treatment is needed. Septic bursitis is caused by the presence of a pus-forming organism, usually staphylococcus aureus. This is confirmed by examining a sample of the fluid in the bursa and requires treatment with antibiotics taken by mouth, injected into a muscle or into a vein (intravenously). The bursa will also need to be drained by needle two or three times over the first week of treatment. When a patient has such a serious infection, there may be underlying causes. There could be undiscovered diabetes, or an inefficient immune system caused by human immunodeficiency virus infection (HIV).
Causes Hammertoe Deformity
 Overview
Overview
hammertoe is the general term used to describe an abnormal contraction or "buckling" of the toe because of a partial or complete dislocation of one of the joints of the toe or the joint where the toe joins with the rest of the foot. As the toe becomes deformed, it rubs against the shoe and the irritation causes the body to build up more and thicker skin to help protect the area. The common name for the thicker skin is a corn.
Causes
The muscles of each toe work in pairs. When the toe muscles get out of balance, a hammer toe can form. Muscle imbalance puts a lot of pressure on the toe's tendons and joints. This pressure forces the toe into a hammerhead shape. How do the toe muscles get out of balance? There are three main reasons. Your genes, you may have inherited a tendency to develop hammer toes because your foot is slightly unstable - such as a flat foot. But high-arched feet can also get hammer toes. Arthritis. Injury to the toe: ill-fitting shoes are the main culprits of this cause. If shoes are too tight, too short, or too pointy, they push the toes out of balance. Pointy, high-heeled shoes put particularly severe pressure on the toes.
 Symptoms
Symptoms
The most obvious symptom of hammertoe is the bent, hammer-like or claw-like appearance of one or more of your toes. Typically, the proximal joint of a toe will be bending upward and the distal joint will be bending downward. In some cases, both joints may bend downward, causing the toes to curl under the foot. In the variation of mallet toe, only the distal joint bends downward. Other symptoms may include Pain and stiffness during movement of the toe, Painful corns on the tops of the toe or toes from rubbing against the top of the shoe's toe box, Painful calluses on the bottoms of the toe or toes, Pain on the bottom of the ball of the foot, Redness and swelling at the joints. If you Hammer toe have any of these symptoms, especially the hammer shape, pain or stiffness in a toe or toes, you should consider consulting your physician. Even if you're not significantly bothered by some of these symptoms, the severity of a hammertoe can become worse over time and should be treated as soon as possible. Up to a point hammertoes can be treated without surgery and should be taken care of before they pass that point. After that, surgery may be the only solution.
Diagnosis
A hammertoe is usually diagnosed with a physical inspection of your toe. Imaging tests, such as X-rays, may be ordered if you have had a bone, muscle, or ligament injury in your toe.
Non Surgical Treatment
If you have hammer toe, avoiding tight shoes and high heels may provide relief. Initial (non-surgical) treatment for hammer toe involves wearing shoes with plenty of room in the toe area. Shoes should be at least one-half inch longer than the longest toe. Stretching and strengthening exercises for the toes (such as picking up items with the toes or stretching the toes by hand) are also recommended. Sometimes orthopedists recommend special pads, cushions, or slings to help relieve the pain of hammer toe.
Surgical Treatment
If your toe is not bendable, your doctor may recommend surgery. The type of surgery that will be performed will depend on the severity of the condition. You should expect blood and urine studies before the procedure, as well as x-rays of your feet. Your doctor will inject either a local or regional anesthetic. If your toe has some flexibility, the doctor may be able to straighten it by simply making an incision in the toe to release or lengthen the tendon. If the toe is not flexible, your doctor will probably make the same incision to release the tendon, but he or she may also remove some pieces of the bone so that the bone can be straightened. A k-wire is placed in the toe to help hold it straight while it is healing. This is taken out after about four weeks.
 Prevention
Prevention
Be good to your feet, because they carry you. They are designed to last a lifetime, but that doesn?t mean they don?t need some love and care as well as some basic maintenance. Check your feet regularly for problems. This is especially true if you have diabetes or any other medical condition that causes poor circulation or numbness in your toes. If you do, check your feet every day so problems can be caught early on. Good circulation is essential. When you're sitting down, put your feet up. If you've been sitting for a while, stretch your legs and feet. Give yourself a foot massage, or ask someone you love for a foot massage. A warm foot bath is also a good idea.
Do Bunions Require Surgical Procedures?
Overview
 A Bunion is one of the most common foot ailments which usually occur near the joint at the base of the big toe. It is actually a bony protrusion which consists of excess or misaligned bone in the joint. Although they may develop on the fifth or little toe, bunions usually occur at the base of the big toe. In addition to causing pain, a bunion changes the shape of your foot, making it harder to find shoes that fit. The good news however, is that you don?t have to hobble for the rest of your life, bunions can be treated.
A Bunion is one of the most common foot ailments which usually occur near the joint at the base of the big toe. It is actually a bony protrusion which consists of excess or misaligned bone in the joint. Although they may develop on the fifth or little toe, bunions usually occur at the base of the big toe. In addition to causing pain, a bunion changes the shape of your foot, making it harder to find shoes that fit. The good news however, is that you don?t have to hobble for the rest of your life, bunions can be treated.
Causes
Despite the popular belief, wearing high heels and too-narrow shoes does not cause bunions. Wearing them can irritate, aggravate, or accelerate the formation of the bunion, but are not the root cause. Bunions are more commonly inherited, if your parents or grandparents had bunions, you may also get one. Bunions can also be caused by trauma or injury to the joints, ligaments, or bones of the foot.
Symptoms
Bunions may or may not cause symptoms. A frequent symptom is foot pain in the involved area when walking or wearing shoes; rest relieves this pain. A bunion causes enlargement of the base of the big toe and is usually associated with positioning of the big toe toward the smaller toes. Shoe pressure in this area can cause interment pain while the development of arthritis in more severe bunions can lead to chronic pain. Bunions that cause marked pain are often associated with swelling of the soft tissues, redness, and local tenderness. It is important to note that, in postpubertal men and postmenopausal women, pain at the base of the big toe can be caused by gout and gouty arthritis that is similar to the pain caused by bunions.
Diagnosis
Clinical findings are usually specific. Acute circumferential intense pain, warmth, swelling, and redness suggest gouty arthritis (see Gout) or infectious arthritis (see Acute Infectious Arthritis), sometimes mandating examination of synovial fluid. If multiple joints are affected, gout or another systemic rheumatic disease should be considered. If clinical diagnosis of osteoarthritic synovitis is equivocal, x-rays are taken. Suggestive findings include joint space narrowing and bony spurs extending from the metatarsal head or sometimes from the base of the proximal phalanx. Periarticular erosions (Martel sign) seen on imaging studies suggest gout.
Non Surgical Treatment
Nonsurgical treatments such as rest and wearing loose (wider) shoes or sandals can often relieve the irritating pain of bunions. Walking shoes may have some advantages, for example, over high-heeled styles that pressure the sides of the foot. Anti-inflammatory medications, such as acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin, Ecotrin), ibuprofen (Advil, Children's Advil/Motrin, Medipren, Motrin, Nuprin, PediaCare Fever) and naproxen (Anaprox, Naprelan, Naprosyn, Aleve), can help to ease inflammation as well as pain. Local cold-pack application is sometimes helpful as well. To reduce tension on the inner part of the joint of a bunion, stretching exercises are sometimes prescribed. Depending on the structure of the foot and severity of the bunion, custom insole orthotics can slow the progression of the bunion and address underlying biomechanical causes. Inflammation of the joint at the base of the big toe can often be relieved by a local injection of cortisone. Any signs of skin breakdown or infection can require antibiotics. When the measures above are effective in relieving symptoms, patients should avoid irritating the bunion again by optimizing footwear and foot care. 
Surgical Treatment
Most bunions can be treated without surgery. But when nonsurgical treatments are not enough, surgery can relieve your pain, correct any related foot deformity, and help you resume your normal activities. An orthopaedic surgeon can help you decide if surgery is the best option for you. Whether you've just begun exploring treatment for bunions or have already decided with your orthopaedic surgeon to have surgery, this booklet will help you understand more about this valuable procedure.
What Are The Principal Reasons For Over-Pronation
Overpronation is the exaggerated inward rolling of the foot and ankle, which can lead to a collapsed arch and flat feet. Many people overpronate and do not even realize it; one way to tell is to simply look at the foot and see how it is placed on the ground when standing in a neutral position. Another way is to wet the bottom of the foot and step on a piece of paper. If the entire imprint of the foot is shown, it means you overpronate.

Causes
Congenital "Flat Feet" - an individual may be born with feet that lack an appropriately supportive arch thereby predisposing the individual to this foot condition. Excessive Weight (Obesity) Too much weight on the foot from either obesity or pregnancy may be a factor. Repetitive Impact walking on flat, hard surfaces continuously places unnatural stress on the foot arch.
Symptoms
Common conditions seen with overpronation include heel pain or plantar fasciitis, achilles tendonopathy, hallus valgus and or bunions, patellofemoral pain syndrome, Iliotibial band pain syndrome, low back pain, shin splints, stress fractures in the foot or lower leg.
Diagnosis
Do the wet foot test. Get your feet wet and walk along a paved surface or sand and look at the footprints you leave. If you have neutral feet you will see a print of the heel with a thin strip connecting to your forefoot, but if you're overpronating your foot print will look a bit like a giant blob with toes.
Non Surgical Treatment
Solutions typically presented will include physical therapy sessions, prolonged prescription drug regimens, occasionally non-traditional approaches like holistic medicine and acupuncture. These options can provide symptom relief in the short term for some patients. However, these treatment methods cannot correct the internal osseous misalignment. Ligaments are not effective in limiting the motion of the ankle bone when excessive joint motion is present. Furthermore, there is not a single, specific ligament that is "too tight" that needs to be "stretched out." The muscles supporting the bones are already being "over-worked" and they cannot be strengthened enough to realign these bones. There is no evidence to suggest that any of these measures are effective in re-establishing or maintaining the normal joint alignment and function.
Surgical Treatment
Subtalar Arthroereisis. Primary benefit is that yje surgery is minimally invasive and fully reversible. the primary risk is a high chance of device displacement, generally not tolerated in adults.
An implant is pushed into the foot to block the excessive motion of the ankle bone. Generally only used in pediatric patients and in combination with other procedures, such as tendon lengthening. Reported removal rates vary from 38% - 100%, depending on manufacturer.
Diagnosing Calcaneal Apophysitis
Sever disease, first described in 1912, is a painful inflammation of the calcaneal apophysis. It is classified with the child and adolescent nonarticular osteochondroses. (The other disease in this group is Iselin disease, which is inflammation of the base of the fifth metatarsal.) The etiology of pain in Sever disease is believed to be repetitive trauma to the weaker structure of the apophysis, induced by the pull of the tendo calcaneus (Achilles tendon) on its insertion. This results in a clinical picture of heel pain in a growing active child, which worsens with activity. Sever disease is a self-limited condition, accordingly, no known complication exists from failure to make the correct diagnosis.
Causes
The foot is one of the first body parts to grow to full size. During the time of growth, bones grow faster than muscles and tendons. This results in the muscles and tendons becoming tight. The strongest tendon that attaches to the heel is the Achilles Tendon. It attaches to the back of the heel at the site of the growth plate, and during sports activities it pulls with great force on the growth plate. If this pull by the tight Achilles Tendon (calf muscle) continues for long periods of time, the growth plate may become inflamed and painful. If exertive activities continue, Sever's Disease may result.
Symptoms
The pain associated with Sever's disease is usually felt along the back of the heel and becomes worse when running or walking. In some children, the pain is so severe they may limp when walking. One of the diagnostic tests for Sever's disease is the "squeeze test". Squeezing both sides of the heel together will produce immediate discomfort. Many children feel pain immediately upon waking and may have calf muscle stiffness in the morning.
Diagnosis
To diagnose the cause of the child?s heel pain and rule out other more serious conditions, the foot and ankle surgeon obtains a thorough medical history and asks questions about recent activities. The surgeon will also examine the child?s foot and leg. X-rays are often used to evaluate the condition. Other advanced imaging studies and laboratory tests may also be ordered.
Non Surgical Treatment
Heel pain, unlike the heel spurs, that occur in adults is very uncommon in children. Of those children who do get heel pain, by far the most common cause is a disturbance to the growing area at the back of the heel bone (calcaneus) where the strong achilles tendon attaches to it. This is known as Sever's disease or calcaneal apophysitis (inflammation of the growth plate). It is most common between the ages of 10 to 14 years of age. These are one of several different 'osteochondroses' that can occur in other parts of the body, such as at the knee (Osgood-Schlatters Disease).
Exercise
For children with Sever's disease, it is important to habitually perform exercises to stretch the hamstrings, calf muscles, and the tendons on the back of the leg. Stretching should be performed 2-3 times a day. Each stretch should be performed for 20 seconds, and both legs should be stretched, even if the pain is only in one heel. Heel cups or an inner shoe heel lifts are often recommended for patient suffering from Sever's disease. Wearing running shoes with built in heel cups can also decrease the symptoms because they can help soften the impact on the heel when walking, running, or standing.
Treatments And Causes
Overview
Tendons do a lot of work. In fact, a great deal of what happens when you walk can be related to tendons tugging and pulling in appropriate ways in their proper places. With this in mind, it?s hardly surprising that on occasion, (probably because we too often forget to send them ?Thank you? cards), tendons may decide that they?ve had it. They may buck their responsibilities, shirk their work, and in all other ways cease to function properly. And that may mean bad news for you. Take the posterior tibial tendon: it runs from the bottom of the calf, goes right under that bump on the inside of the ankle (the medial malleolus) and ends up attaching itself to a bone on the inside of the middle of your foot (the navicular bone). It?s the main tendon that keeps the arch of your foot in place, and it helps a bunch in walking, too. Over time, though, we tend to put a lot of stress on this faithful tendon, especially if we?ve put on extra weight, or do a lot of activities that stress it out, walking, running, hiking, or climbing stairs. Sometimes athletes (who do a lot of that walking and running stuff) may put so much stress on the tendon that it tears suddenly. But for many of us, damage may take place gradually (i.e. the tendon stretches out) until the tendon tells us that it flat out quits. (It sometimes doesn?t even give two weeks notice.) In short, you may develop posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD). 
Causes
As discussed above, many different problems can create a painful flatfoot. Damage to the posterior tibial tendon is the most common cause of AAFD. The posterior tibial tendon is one of the most important tendons of the leg. It starts at a muscle in the calf, travels down the inside of the lower leg and attaches to the bones on the inside of the foot. The main function of this tendon is to support the arch of your foot when you walk. If the tendon becomes inflamed or torn, the arch will slowly collapse. Women and people over 40 are more likely to develop problems with the posterior tibial tendon. Other risk factors include obesity, diabetes, and hypertension. Having flat feet since childhood increases the risk of developing a tear in the posterior tibial tendon. In addition, people who are involved in high impact sports, such as basketball, tennis, or soccer, may have tears of the tendon from repetitive use. Inflammatory arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, can cause a painful flatfoot. This type of arthritis attacks not only the cartilage in the joints, but also the ligaments that support the foot. Inflammatory arthritis not only causes pain, but also causes the foot to change shape and become flat. The arthritis can affect the back of the foot or the middle of foot, both of which can result in a fallen arch. An injury to the tendons or ligaments in the foot can cause the joints to fall out of alignment. The ligaments support the bones and prevent them from moving. If the ligaments are torn, the foot will become flat and painful. This more commonly occurs in the middle of the foot (Lisfranc injury), but can also occur in the back of the foot. Injuries to tendons of the foot can occur either in one instance (traumatically) or with repeated use over time (overuse injury). Regardless of the cause, if tendon function is altered, the forces that are transmitted across joints in the foot are changed and this can lead to increased stress on joint cartilage and ligaments. In addition to tendon and ligament injuries, fractures and dislocations of the bones in the midfoot can also lead to a flatfoot deformity. People with diabetes or with nerve problems that limits normal feeling in the feet, can have collapse of the arch or of the entire foot. This type of arch collapse is typically more severe than that seen in patients with normal feeling in their feet. In addition to the ligaments not holding the bones in place, the bones themselves can sometimes fracture and disintegrate without the patient feeling any pain. This may result in a severely deformed foot that is very challenging to correct with surgery. Special shoes or braces are the best method for dealing with this problem.
Symptoms
At first you may notice pain and swelling along the medial (big toe) side of the foot. This is where the posterior tibialis tendon travels from the back of the leg under the medial ankle bone to the foot. As the condition gets worse, tendon failure occurs and the pain gets worse. Some patients experience pain along the lateral (outside) edge of the foot, too. You may find that your feet hurt at the end of the day or after long periods of standing. Some people with this condition have trouble rising up on their toes. They may be unable to participate fully in sports or other recreational activities.
Diagnosis
The history and physical examination are probably the most important tools the physician uses to diagnose this problem. The wear pattern on your shoes can offer some helpful clues. Muscle testing helps identify any areas of weakness or muscle impairment. This should be done in both the weight bearing and nonweight bearing positions. A very effective test is the single heel raise. You will be asked to stand on one foot and rise up on your toes. You should be able to lift your heel off the ground easily while keeping the calcaneus (heel bone) in the middle with slight inversion (turned inward). X-rays are often used to study the position, shape, and alignment of the bones in the feet and ankles. Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging is the imaging modality of choice for evaluating the posterior tibial tendon and spring ligament complex.
Non surgical Treatment
In the early stages, simple pre-fabricated orthotics can help improve the heel position to reduce the mechanical load which is contributing to the symptoms. In advanced stages or long term orthotic use, a plaster of paris or foam box cast can be taken and specific bespoke orthotics manufactured. If the condition develops further a AFO (ankle foot orthotic) may be necessary for greater control. In more advanced stages of symptomatic Adult Acquired flat feet, where the conservative methods of treatment have failed there are various forms of surgery available depending upon the root cause of the issue and severity. 
Surgical Treatment
Good to excellent results for more than 80% of patients have been reported at five years' follow up for the surgical interventions recommended below. However, the postoperative recovery is a lengthy process, and most surgical procedures require patients to wear a plaster cast for two to three months. Although many patients report that their function is well improved by six months, in our experience a year is required to recover truly and gain full functional improvement after the surgery. Clearly, some patients are not candidates for such major reconstructive surgery.